Table of Contents
Even the best of developers can go wrong sometimes, but what makes them great is knowing undoing changes in Git quickly and safely. Committed wrong code, merged too soon, or accidentally edited the wrong file, and suddenly, you feel lost and stuck. Git offers reset, revert, and checkout to help.
And in this article, you will get to learn places these commands differ, their real-world use cases, and how you can recover your code using Git version control with confidence. By the end of it, you will learn how to undo the last commit in Git, roll back merges, and checkout previous commits without risks.
Why Do You Need to Undoing Changes in Git?
Simply speaking, version control is the way to keep a check on changes while having a good compromise on collaborating. But mistakes happen. You may:
- Commit the wrong file
- Merge the wrong branch
- Push broken code
- Modify or delete important lines
This is where all that undo magic of GIT comes in. But before everyone knows them, understanding their purpose and limitations becomes pretty important.
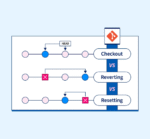
Understanding the Basics: Reset vs Revert vs Checkout
We’ll quickly run through what each one does, and then look at some examples.
➤ git reset
Changes the commit history of your branch: either unstaging the changes or removing some commits.
➤ git revert
Adds a new commit that undoes the effects of a past commit and is safe for public/sharing branches.
➤ git checkout
A way to view or go back to a previous commit or branch; also for discarding changes.
How to Undo Last Commit in Git
Depending on whether or not you’ve pushed the last commit and whether you want to keep the changes on your working directory or not, you’ll have different ways to undo the last commit in Git.
➤ Option 1: Soft Reset (Keeps changes)
git reset –soft HEAD~1
This goes back by one commit but keeps the changes in the staging area. This is a great option for situations in which you forgot to change a message or add something on a commit.
➤ Option 2: Mixed Reset (Unstages but keeps code)
git reset –mixed HEAD~1
It unstages the files but does not delete them from the working directory.
➤ Option 3: Hard Reset (Dangerous!)
git reset –hard HEAD~1
This rolls back the last commit along with its changes—use with caution.
Pro Tip: Understand what a git reset soft or hard can do for you before you actually use it. A soft reset is safe and reversible while a hard reset is irreversible once run.
Use these options wisely when figuring out how to undo last commit in Git.
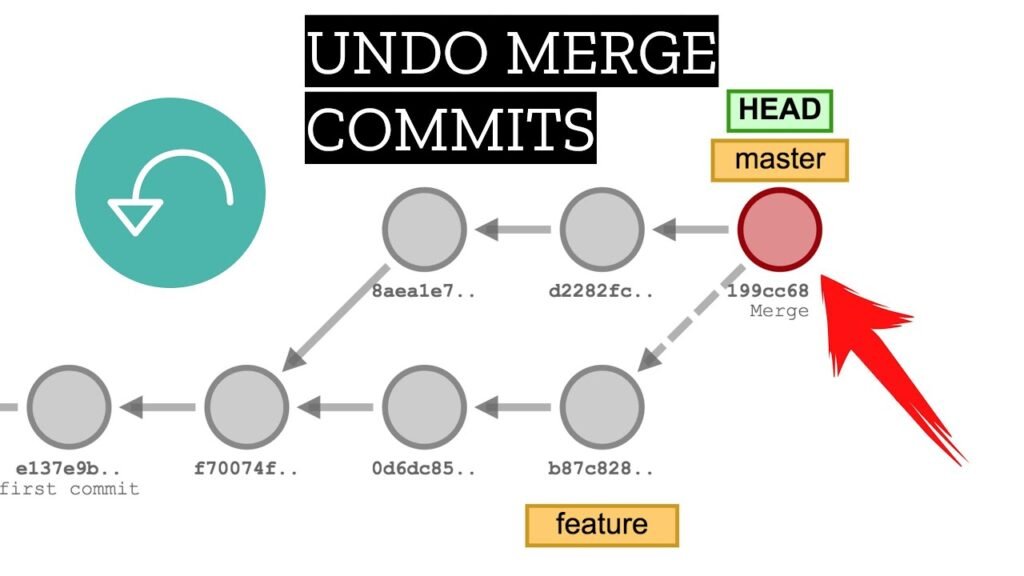
Undo Merge in Git
Suppose you’ve accidentally merged a feature branch into your main branch- what do you do now?
➤ Option 1: Revert the merge commit
If you’ve already pushed the merge:
git revert -m 1 <merge-commit-hash>
It is the safest method to undo merge in Git on shared branches as it keeps the history and reverts the changes by an additional commit.
➤ Option 2: Reset to previous commit
If the merge hasn’t been pushed:
git reset –hard HEAD~1
This will delete the merge commit and all changes from it. However be cautious since this may affect those who have already pulled it down.
Knowing how to undo merge in Git can save hours of head scratching and confusion among team members.
Git Checkout Previous Commit: When and How
“Checking out” a previous commit means to go back in time and see your project as it was in that specific moment without changing anything in history. This is where the checkout command shines.
➤ View Previous Commit
git checkout <commit-hash>
This puts your working copy into a previous commit snapshot. Your repo has now entered the so-called “detached HEAD” state.
➤ Restore a File from Previous Commit
git checkout <commit-hash> — path/to/file
This one allows you to recover deleted or modified files from an older commit without checking out another branch.
➤ Create a Branch from Old Commit
If you want to work from that older state:
git checkout -b old-state <commit-hash>
You’ll use git checkout previous commit often for debugging, hotfixes, and time-travel-style development.
Always create a new branch if you plan to make changes after checking out a previous commit.
Git Undo Commit Without Losing Code
Sometimes you just want to undo a commit but not lose your code. That’s where reset –soft shines again.
git reset –soft HEAD~1
This undoes the last commit, sending your changes to the staging area. This is the ideal command to use when fixing typos, adding forgotten files, or changing commit messages.”
You can also use:
git commit –amend
This edits the last commit without touching your code.If you’re wondering how to git undo commit cleanly, these are your go-to tools.
Git Reset Soft vs Hard: Know the Risk
Let’s compare the two directly:
| Command | Keeps Code? | Keeps Staging? | Safe to Use? |
| –soft | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| –mixed | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| –hard | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⚠️ Dangerous |
The choice between git reset soft vs hard depends on how much you want to remove. Never use –hard unless you’re absolutely sure!
Summary: Which Command to Use When?
| Task | Best Command |
| Undo last commit (keep code) | git reset –soft HEAD~1 |
| Undo last commit (delete code) | git reset –hard HEAD~1 |
| Undo commit on shared branch | git revert <commit> |
| View previous commit | git checkout <commit> |
| Undo file changes | git checkout — file |
| Undo accidental merge | git revert -m 1 <hash> or reset |
Understanding how to undo changes in Git is essential for clean workflows, bug fixes, and confident collaboration.
You can view other articles in our website here.






To create an account in various services, you often need number 4 sms, which can help in keeping your personal information safe.
Temporary phone numbers are increasingly used by individuals and companies for security purposes . This trend is particularly noticeable among those who frequently use online services, as temporary phone numbers can be used to verify accounts without revealing personal contact information. Online account verification is a common use for temporary phone numbers, providing an extra layer of privacy. Furthermore, temporary phone numbers can be used for a variety of purposes, including receiving SMS messages and making calls, all while keeping the user’s real phone number hidden. The functionality of temporary phone numbers includes receiving SMS messages, making voice calls, and other uses, all while keeping the user’s phone number confidential.
In addition to their practical applications, temporary phone numbers have also become essential for individuals who value their privacy and wish to avoid unwanted communications. Many individuals opt for temporary phone numbers as a means to protect their personal privacy and avoid unwanted calls and messages . This is especially true in cases where personal contact information is required for services that may potentially misuse it. Temporary phone numbers offer a secure way to provide contact information without the risk of it being misused by services . By using a temporary phone number, individuals can ensure that their real phone number remains confidential and is not shared with unwanted parties. The use of temporary phone numbers guarantees that the user’s actual phone number is kept confidential and not distributed to unwanted parties.
Benefits of Temporary Phone Numbers
The benefits of temporary phone numbers are multifaceted, ranging from enhanced privacy to convenience. The primary benefit of using temporary phone numbers is the increased privacy they provide. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who are concerned about their personal information being accessed by unauthorized parties. Temporary phone numbers are especially useful for those who are worried about their personal data being accessed without authorization . Additionally, temporary phone numbers can be easily discarded and replaced, making them ideal for short-term use. Temporary phone numbers are convenient because they can be discarded and replaced as needed, which is ideal for short-term applications.
Another significant benefit of temporary phone numbers is their ability to prevent spam and unwanted communications. Temporary phone numbers are effective in preventing spam and unwanted communications from reaching the user . By using a temporary phone number, individuals can significantly reduce the amount of unwanted calls and messages they receive. The use of temporary phone numbers leads to a substantial decrease in the amount of unwanted calls and messages. This not only enhances the user’s privacy but also reduces the risk of falling victim to scams and phishing attempts. The use of temporary phone numbers not only enhances user privacy but also minimizes the risk of falling prey to scams and phishing attempts .
Applications of Temporary Phone Numbers
Temporary phone numbers have a wide range of applications, from personal use to business applications. The applications of temporary phone numbers are diverse, ranging from personal to commercial use . For personal use, temporary phone numbers can be used to sign up for services that require a phone number for verification, without having to provide a real phone number. The use of temporary phone numbers for personal purposes includes signing up for online services that necessitate phone verification. This is particularly useful for individuals who are concerned about their privacy and do not want to receive unwanted communications. The use of temporary phone numbers for personal purposes is especially beneficial for those who prioritize their privacy and want to minimize unwanted contacts .
In business applications, temporary phone numbers can be used to provide customer support without revealing the company’s main contact information. The use of temporary phone numbers in business allows companies to provide customer support while keeping their main contact information confidential. This can help in maintaining the privacy of the company’s internal communications and preventing unwanted solicitations. The use of temporary phone numbers for customer support helps businesses maintain the privacy of their internal communications and reduces unwanted solicitations . Furthermore, temporary phone numbers can be used for marketing campaigns, allowing businesses to track the effectiveness of their advertisements without compromising their main phone number. Temporary phone numbers can be used for marketing campaigns to track advertisement effectiveness without compromising the main phone number .
Conclusion and Future of Temporary Phone Numbers
In conclusion, temporary phone numbers have become an essential tool for both personal and business use, offering a range of benefits from enhanced privacy to convenience. Temporary phone numbers have evolved into a crucial instrument for individuals and businesses, offering advantages such as improved privacy and ease of use . As the demand for privacy and security continues to grow, the use of temporary phone numbers is expected to increase. The increasing demand for privacy and security is expected to lead to a higher adoption rate of temporary phone numbers .
The future of temporary phone numbers looks promising, with advancements in technology expected to further enhance their functionality and accessibility. Temporary phone numbers are expected to have a bright future, with technology updates likely to enhance their usability and availability . As more individuals and businesses become aware of the benefits of temporary phone numbers, their adoption is likely to become more widespread. With growing awareness of the benefits offered by temporary phone numbers, it is expected that their use will become more prevalent among individuals and companies. This, in turn, is expected to drive innovation in the field, leading to the development of more sophisticated and user-friendly temporary phone number services. The growing use of temporary phone numbers is likely to foster innovation, leading to the development of more complex and easy-to-use temporary phone number services.
Looking for an experienced full-time next.js freelancer for your project?
The Next.js framework is gaining popularity among developers. One of the major advantages of this framework is its ability to create server-rendered applications.
First and foremost, Next.js includes automatic code splitting, which enhances the efficiency of applications. This optimization allows for faster page loading, enhancing user experience.
Another significant feature of Next.js is its built-in routing. Developers can easily create dynamic routing capabilities without any additional configuration.
Another aspect worth noting is the robust Next.js community that offers extensive support. Forums, tutorials, and documentation are readily available, ensuring developers can overcome challenges.